Investing in real estate can be a lucrative way to build wealth, but it also comes with risks. One way to mitigate those risks is through insurance. In this blog post, we’ll explore insurable risks when investing in real estate and how insurance can help protect your investment. We’ll also discuss deductible size, self-insuring, and other ways to manage risk. But first, let’s take a look at some of the most common insurable risks when investing in real estate.
What are your fears relating to investing in real estate?
Risk Matrix

The risk matrix image is a 3×3 matrix that includes high, medium, and low risk categories, as well as likelihood and impact scales. The matrix is used to evaluate risks and determine whether action is necessary to mitigate the risk. The likelihood scale ranges from rare to frequent, while the impact scale ranges from minor to catastrophic. The matrix is color-coded to indicate the level of risk, with red indicating high risk, yellow indicating medium risk, and green indicating low risk.
Insurance
Insurance is a way to transfer risk from yourself to a third party in exchange for a fee. This is particularly useful for insurable risks that happen infrequently but can be very expensive when they do happen, such as fire, lightning damage, hail damage, theft, vandalism, personal injury, and liability. By paying a relatively small fee, you can have a third party insurance company cover you in case of such events, and they can use the pool of money they collect from others to pay out claims.
For real estate investors, insurance is an important consideration, particularly when it comes to protecting against catastrophic events like a house burning down. While some investors may choose to self-insure, for most it makes more sense to pay a third party insurance company to take on the risk. This is especially true for smaller investors who may not have enough properties to effectively self-insure.
When considering insurance, it’s important to evaluate the likelihood and severity of potential risks. Some risks, like a tenant paying rent late, may be relatively likely but not severe enough to warrant insurance. Other risks, like a fire, may be less likely but have the potential to cause catastrophic losses. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to purchase insurance will depend on the individual investor’s risk tolerance and financial situation.
It’s also important to understand the specific terms and coverage of your insurance policy. Insurance policies may have deductibles, limits, and exclusions that can impact their effectiveness in protecting against certain risks. Working with an experienced insurance agent can help ensure that you understand your policy and are adequately protected.
In summary, insurance is a valuable tool for real estate investors looking to protect against catastrophic losses. By transferring risk to a third party in exchange for a fee, investors can mitigate the financial impact of events like fires, theft, and personal injury. However, it’s important to carefully evaluate the likelihood and severity of potential risks and to understand the specific terms and coverage of your insurance policy.
Insurable Risks
Here are some of the more commonly insured risks that real estate investors can purchase insurance for:
- Fire: Insurance can cover the cost of damage caused by a fire on your property. The likelihood of this happening is low, but the payout can be significant if it does occur.
- Lightning: Similar to fire, insurance can cover the cost of damage caused by lightning striking your property.
- Hail: Insurance can cover the cost of damage caused by hail, such as damage to the roof, windows, or siding.
- Theft: Insurance can cover the cost of theft, such as stolen appliances or HVAC units.
- Vandalism: Insurance can cover the cost of damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti or damage to the interior or exterior of the property.
- Personal Injury: Insurance can cover the cost of injuries sustained by others on your property, such as slip-and-fall accidents.
- Liability: Insurance can cover the cost of damages or injuries caused by your actions or negligence, such as a guest getting injured on your property.
It’s important to note that not all insurance policies cover all of these risks. It’s also important to discuss your specific needs with an insurance agent to ensure you have adequate coverage. Additionally, there are some less commonly insured risks that investors may want to consider as well.
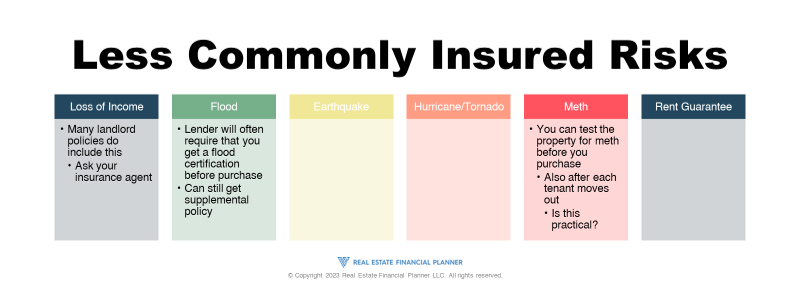
Less Commonly Insured Risks
When it comes to insurance coverage for real estate investments, most people are aware of the commonly insured risks such as fire, theft, and personal injury liability. However, there are also less commonly insured risks that investors can purchase insurance for. These risks may not occur as often, but can be very expensive when they do.
One of these risks is loss of income. This type of insurance coverage is for the inability to collect rent due to the condition of the property. For example, if a property suffers from a fire or other disaster, and the owner is unable to collect rent while waiting for repairs, this type of insurance can provide coverage for the lost income. Many landlord policies do include loss of income coverage, but it’s important to ask your insurance agent about this type of coverage to ensure you have adequate protection.
Another less commonly insured risk is flood damage. If a property is in a flood zone, the lender may require a flood certification before purchase, and may also require flood insurance to protect their investment. However, investors can also choose to purchase supplemental policies to provide additional coverage for flood damage. It’s important to note that just because a property is not in a federally recognized flood zone, it does not mean that it is not at risk for flooding. Unexpected events can occur, such as water running horizontally from a neighbor’s property, which could cause damage to your property.
Earthquake insurance is another less commonly insured risk. This type of insurance provides coverage for damages caused by earthquakes. While earthquakes may not be common in all areas, they can cause significant damage and can be very expensive to repair.
Hurricanes and tornadoes can also cause significant damage to properties, and insurance policies can be purchased to provide coverage for these risks. In areas where these types of weather events are more common, it may be wise to consider this type of insurance.
Meth insurance is another less commonly insured risk. If a tenant is using or producing meth in a rental property, it can cause significant damage and can be expensive to repair. Meth insurance provides coverage for these damages, and investors can choose to test the property for meth before purchase, and also after each tenant moves out.
Finally, rent guarantee insurance can provide coverage to guarantee rental income. This type of insurance is for investors who are concerned that their tenants may not be able to pay rent due to job loss or other reasons. While some investors may choose to set aside money in reserves to cover potential lost rent, others may choose to purchase rent guarantee insurance for added protection.
It’s important to note that not all insurance policies will cover these less commonly insured risks, so it’s important to ask your insurance agent about your specific coverage options. By understanding the risks and purchasing the appropriate insurance coverage, investors can protect their investments and their income.
Deductible Size
When it comes to insurable risks in real estate investment, having insurance can protect you from catastrophic losses. However, the size of your deductible can have a significant impact on your insurance premiums. If you have a low tolerance for risk, you may choose to keep your deductible low, which means that you will need to pay less out of pocket if you file a claim. However, this will result in higher insurance premiums.
On the other hand, if you have a high tolerance for risk, you can choose to have a higher deductible. This will lower your insurance premiums but will mean that you will need to pay more out of pocket if you file a claim. One strategy is to partially “self-insure” by having a higher deductible, lower insurance premiums, and paying for smaller claims out of pocket.
It is recommended to only file a claim if the cost of repairs is 2 or 3 times your deductible amount. Keep in mind that there are exceptions to this rule of thumb, and you should be prepared to pay out of pocket for repairs if necessary. It is also important to note that making frequent claims can result in higher premiums and fewer coverage options, as insurance companies may opt not to renew your policy or decline coverage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, investing in real estate comes with risks, but insurance can help mitigate those risks. It’s important to understand the specific insurable risks associated with real estate investing, and to evaluate the likelihood and severity of potential risks when considering insurance. Deductible size is another important factor to consider when purchasing insurance, as it can have a significant impact on premiums and out-of-pocket expenses. While insurance is an important tool for managing risk, it’s not the only one. Self-insuring, maintaining reserves, and careful property selection are all important factors to consider when investing in real estate. By understanding the risks and taking steps to manage them, investors can protect their investments and their financial futures.