Ready to unlock the secrets of creative financing in real estate investing? You’re about to embark on an exciting journey that could revolutionize your approach to property acquisition. Creative financing isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a powerful set of strategies that can help you bypass traditional bank loans and mortgages.
Imagine being able to invest in real estate with little to no money down, or structuring deals that work for both you and the seller. That’s the power of creative financing. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, these non-traditional methods can open doors to opportunities you might have thought were out of reach.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore six types of creative transactions that could transform your real estate investing game. You’ll learn about owner financing, wrap financing, loan assumptions, and more. We’ll dive into the benefits and potential pitfalls of each strategy, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Remember, with great power comes great responsibility. As we delve into these strategies, keep in mind that the goal is always to create win-win situations. So, are you ready to expand your real estate investing toolkit? Let’s dive in!
6 Types of Creative Transactions
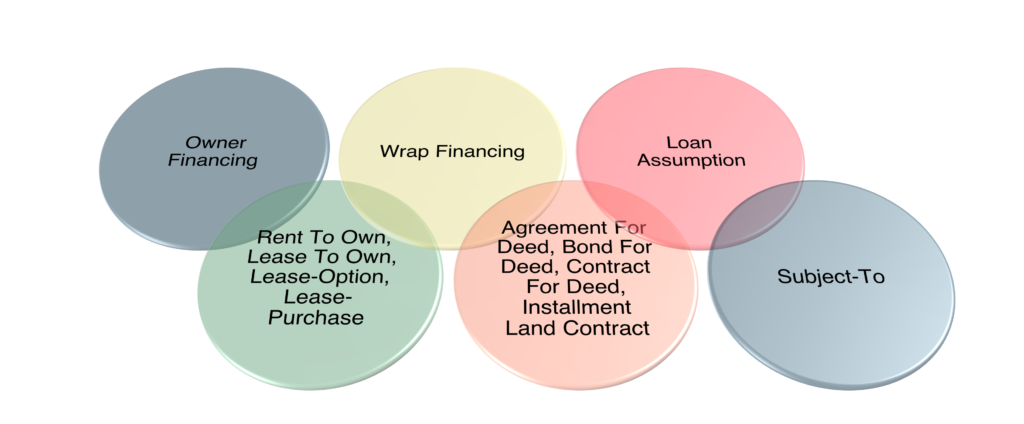
Let’s dive into the different types of creative financing options available to real estate investors. Each of these strategies offers unique advantages and considerations:
- Owner Financing – In this scenario, the seller acts as the bank. They don’t have a mortgage on the property and offer to finance the purchase for you.
- Wrap Financing – Here, the seller has an existing mortgage and “wraps” that mortgage by offering you owner financing. It’s similar to a subject-to transaction (which we will cover shortly), but the seller retains the right to foreclose if you don’t make payments.
- Loan Assumption – With this method, you formally take over responsibility for the seller’s loan with the lender’s permission. This can be particularly advantageous if the existing loan has a lower interest rate than current market rates.
- Rent-To-Own Family – Generically, you’re renting the property with the right to be an owner of the property later. These options can be great if you need time to improve your financial situation before purchasing or you’re uncertain what the market will do. This category includes several variations:
- Lease-Option – You have a lease agreement with an option to purchase the property.
- Lease-Purchase – Similar to a lease-option, but with a purchase contract included.
- Agreement for Deed Family – This includes variations like Agreement for Deed, Bond for Deed, Contract for Deed, and Installment Land Contract. In these arrangements, you make payments over time, but the deed isn’t transferred until you’ve fulfilled the terms of the agreement. This can be useful for sellers who want to ensure you can meet the financial obligations before transferring ownership.
- Subject To – In this arrangement, you buy the property from the seller, they deed it to you, and you make payments on the seller’s existing loan. This can be a powerful strategy, especially if the existing loan has favorable terms.
Remember, each of these strategies comes with its own set of risks and rewards.
It’s crucial to thoroughly understand the terms and implications of any creative financing arrangement before proceeding and that’s what we will cover here.
Win-Win or No Deal
“With great power comes great responsibility.” – Uncle Ben from Spider-Man
In real estate investing, always aim for win-win deals. It’s not just ethical; it’s smart business. By ensuring both parties benefit, you build trust, reduce legal risks, and create long-term success. Remember, your reputation is your most valuable asset. If a deal doesn’t feel right for everyone involved, be prepared to walk away. There will always be other opportunities that align with this principle.
Benefits of Creative Financing
Let’s explore why you might want to consider these innovative approaches:
- Minimal Down Payment – Unlike traditional financing that often requires 20-25% down, creative financing can sometimes be done with little to no money down. This allows you to preserve your capital for other investments, improving cash flow or improvements.
- Bypass Bank Qualifications – Most creative financing variations allow you to purchase properties without going through rigorous bank qualifications (with a notable exception being loan assumptions). This can be especially beneficial if you have credit blemishes (bankruptcy, foreclosures, short sales) or irregular income. It is a best practice to disclose all material facts when structuring deals.
- Flexibility in Ownership Structure – You can often buy properties in an LLC or other entity upfront, which can provide valuable asset protection and tax benefits.
- Amplified Returns – By using less of your own capital, you can potentially see higher returns on your investment. This leverage can significantly boost your wealth-building potential. Be aware though that small down payments and small amounts invested can also amplify losses as well.
- Exit Strategy Options – Many creative financing deals offer more flexible exit strategies. If a property isn’t performing as expected, you may have more options to walk away compared to traditional financing. For example, rent-to-owns could be structured such that if the market declines during your rent period, you do not need to purchase the property.
- Retirement Account Investing – Creative financing can sometimes allow you to use self-directed IRAs or 401(k)s to invest in real estate without needing the typical 30-35% down payment or partners.
- Partnership Opportunities – These strategies can open doors to partnerships, allowing you to invest in properties without a credit partner. You could work on improving your financial situation (increase income, save down payment, improve credit, establish job history, accumulate tax returns, etc) for future traditional purchases while investing creatively in the meantime.
- Reduced Capital Expenditure Risk – The nature of many creative financing deals encourages shorter hold times, which can reduce your exposure to major capital expenditures.
Downsides of Creative Financing
And why you might want to consider NOT doing these types of deals…
Here are some key reasons to consider not using creative financing deals:
- Limited selection of properties – Buying traditionally allows you to pick from a larger pool of properties on the open market. Creative financing often restricts you to motivated sellers, potentially limiting your options.
- More labor-intensive to buy – Creative deals often require extensive marketing, searching, negotiations and some additional due diligence. This can be time-consuming compared to traditional purchases from within the MLS.
- Lower ROI for time invested – The effort required to find and structure creative deals may not always justify the returns. Your time might be better spent on other activities or other investment activities.
- Potential legal and ethical risks – Some creative financing structures can be complex and may inadvertently cross into questionable legal and ethical territory.
- Implied Shorter Duration – Some creative financing implies a shorter time frame. For example, rent-to-own might give a limited time to decide to buy the property.
Jargon Versus General Discussion
For our discussions here, I’ll use real estate investing jargon but you should not use jargon when talking to your sellers.
We’ll discuss things like:
- Subject-To – This refers to buying a property subject to the existing financing.
- After Repair Value (ARV) – The estimated value of a property after renovations are completed.
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) – The ratio of a loan to the value of an asset purchased.
- Return on Investment (ROI) – A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment.
However, when you’re talking to sellers, it’s crucial to switch gears.
Most sellers aren’t real estate professionals, so using jargon can be confusing or even intimidating.
Instead, use plain language that anyone can understand.
For example, instead of saying:
“I’ll buy it Subject-To and give you $5K for your equity”
You might say:
“I’ll buy the house and take care of your mortgage payments. Plus, I’ll give you $5,000 at closing.”
This approach has two benefits:
- Clear communication – The seller understands exactly what you’re proposing without needing to learn new terms.
- Flexibility – By using general terms, you’re not locking yourself into a specific strategy before you’ve had a chance to analyze the deal fully.
Remember, your goal is to solve the seller’s problem, not to impress them with your real estate knowledge. By speaking their language, you’re more likely to build trust and close the deal.
Here’s another example of how you might approach a seller:
“What if I covered the monthly payments on your loan and took care of the property maintenance so you wouldn’t have to worry about that? Is that something that would work for you?”
This simple question could potentially lead to various creative financing strategies, such as a Subject-To deal, a lease option, or even owner financing. The key is to start the conversation in a way that the seller can easily understand and relate to.
By mastering both the technical jargon for your own understanding and the plain language for seller communication, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the world of creative real estate financing.
You Are Not Your Sellers
Whether or not you would do something is not a reflection of what others would do.
Just because you wouldn’t do something doesn’t mean someone else wouldn’t do it. Just because you would do something, doesn’t mean that someone else would do it.
You are not your sellers.
Why Would Sellers Do Creative Financing?
While not a comprehensive list, let’s explore some common motivations and why sellers might do creative financing:
- Solving financial problems – Creative financing can help sellers who are struggling to make mortgage payments or facing foreclosure. It provides a way out of their financial bind while potentially preserving their credit.
- Quick property sale – For sellers who need to move quickly due to job relocation or other life changes, creative financing can attract more buyers and speed up the selling process.
- Maximizing sale price – By offering flexible terms, sellers may be able to command a higher sale price than they would in a traditional cash sale.
- Generating income – Owner financing or wrap-around mortgages can provide sellers with a steady income stream, which can be particularly attractive for retirees or those looking for passive income.
- Avoiding capital gains taxes – Installment sales can spread out the tax liability over several years, potentially reducing the overall tax burden for the seller.
- Emotional relief – For properties associated with difficult memories (e.g., divorce or death of a loved one), creative financing can offer a quicker exit strategy, allowing sellers to move on emotionally.
- Maintenance freedom – Sellers who no longer want the responsibility of property management can use options like lease-purchases to transfer most maintenance duties to the buyer.
- Market conditions – In a buyer’s market where traditional sales are slow, creative financing can make a property stand out and attract more potential buyers.
Remember, every seller’s situation is unique. As an investor, your job is to listen carefully and structure a deal that addresses their specific needs and concerns while also benefiting you.
Why Wouldn’t Sellers Do Creative Financing?
While creative financing can be an attractive option for many real estate transactions, some sellers might be hesitant to engage in these deals. Let’s explore some of the reasons why:
- Not a good fit for their situation – Some sellers may need a lump sum of cash immediately for various reasons, such as paying off debts or purchasing another property. Creative financing options that involve payments over time might not meet their immediate financial needs.
- Fear of potential risks – Sellers may have concerns about:
- Property damage – They might worry about tenants or buyers not maintaining the property properly, potentially decreasing its value.
- Payment issues – There’s a fear that buyers might stop making payments, leading to a complicated and costly legal process.
- Ongoing involvement – Some sellers want a clean break and don’t want to deal with ongoing financial ties to the property.
- Social perceptions – They might be concerned about what friends, family, or neighbors would think about unconventional selling methods.
- Unrealistic expectations – Some sellers may have inflated ideas about their property’s value or market conditions:
- Overvaluing their property – They might believe their home is worth more than comparable properties in the area.
- Expecting a quick, full-price cash offer – Sellers might think they’ll receive multiple cash offers at or above asking price.
- Blaming marketing – If the property isn’t selling, they might think it’s due to poor marketing rather than pricing or property issues.
- Emotional attachment – Sellers who have a strong emotional connection to their property might set an unrealistic price based on personal value rather than market value.
- Preference for traditional transactions – Many sellers are more comfortable with conventional selling methods:
- Familiarity – Traditional sales processes may be well-understood and feel less risky to many sellers.
- Quick closure – Some sellers prefer the idea of a clean, one-time transaction rather than an ongoing financial relationship.
- Professional guidance – Working with real estate agents and traditional lenders can provide a sense of security and expert advice throughout the process.
Understanding these potential objections can help you address sellers’ concerns and find creative solutions that work for both parties.
Remember, successful creative financing deals often require clear communication, patience, and a willingness to find win-win scenarios.
Owner Financing

Owner Financing: What is it?
Owner financing is a creative real estate strategy where the seller acts as the bank, providing financing for the buyer to purchase their property. This approach can be particularly advantageous for investors looking for alternative financing options.
Here’s how owner financing typically works:
- Seller as the Bank – The property must be owned free and clear by the seller. This means there’s no existing mortgage on the property. If there is an existing loan, it would be considered wrap financing instead.
- Property Purchase – You, as the buyer, purchase the property directly from the seller. The transaction is similar to a traditional sale, but the financing comes from the seller rather than a bank.
- Negotiated Terms – You and the seller agree on the terms of the loan. This includes the interest rate, loan duration, purchase price, payment schedule, and whether there’s a balloon payment. You may also negotiate the amortization schedule.
- Legal Documentation – The agreement is formalized with a promissory note and a deed of trust (or mortgage in some markets) for the benefit of the seller. This provides legal protection for both parties.
- Ownership and Responsibility – You become the owner of the property. However, if you fail to make payments as agreed, the seller has the right to foreclose, just like a bank would in a traditional mortgage scenario.
Owner financing can offer flexibility that traditional lenders can’t match. For example, you might negotiate a lower interest rate, a longer repayment term, or more favorable qualification criteria.
Some advanced strategies in owner financing include:
- Substitution of Collateral – This strategy allows you to potentially swap the property securing the loan with another property, providing flexibility in your investment portfolio.
- Leveraging Other Financing – You might use a private money or hard money loan as a down payment, putting the seller in second position. This can help you acquire properties with less of your own capital upfront.
Key Characteristics of Owner Financing Sellers
When you’re looking for owner financing opportunities, understanding the characteristics of potential sellers is crucial. Here’s what you need to know:
- Free and clear ownership – More than one-third of all homes in the US are owned without a mortgage. These sellers have the flexibility to offer you owner financing directly.
- Ability to pay off existing mortgages – Some sellers may be willing to pay off their current mortgage to offer you owner financing, expanding your pool of potential deals.
- Motivated sellers – Look for properties that have been on the market for a long time, are vacant, or aren’t being maintained. These sellers may be more open to creative financing options.
- Out-of-area owners – Sellers who live far from their property might prefer the steady income of owner financing over the hassles of long-distance property management.
- Income-seeking sellers – Some property owners are looking for a reliable income stream. Owner financing can provide them with regular payments, often at a higher interest rate than they’d get from other investments.
- Equity-focused sellers – Owners with significant equity in their property might be interested in converting that equity into an income-producing asset through owner financing.
Remember, each seller’s situation is unique. By understanding these common characteristics, you’ll be better equipped to identify and approach potential owner financing opportunities in your real estate investing journey.
Benefits To Seller of Owner Financing
Owner financing isn’t just beneficial for buyers; it offers several advantages to sellers as well. As an investor buyer, understanding these benefits can help you identify motivated sellers and structure win-win deals.
Let’s explore why a seller might consider this creative financing option:
- Quick sale – By offering owner financing, sellers can attract a larger pool of potential buyers like you, potentially selling their property faster. This can provide peace of mind for sellers, especially if they’ve been struggling to sell through traditional methods.
- Marketing edge – Sellers advertising their property with owner financing can make it stand out in a competitive market. This unique selling proposition can attract buyers like you who might not qualify—or want to qualify—for traditional mortgages.
- Steady income stream – Instead of receiving a lump sum, sellers get regular monthly payments from you. This can be particularly attractive for sellers looking for a consistent income source, perhaps to supplement their retirement.
- Higher returns – Sellers might earn a higher return on their property compared to selling outright and investing the proceeds in low-yield options like CDs or savings accounts. The interest rate on owner financing is often higher than what they’d earn from these traditional investments.
- Tax benefits – Owner financing can offer tax advantages to sellers by spreading their capital gains over several years instead of incurring them all in one tax year. Always encourage sellers to consult with a tax professional to understand how this applies to their specific situation.
- Flexible terms – As the financier, sellers have the flexibility to negotiate terms that work best for them, including interest rates, loan duration, and payment schedules. This can create opportunities for you as a buyer to structure a deal that works for both parties.
Qualifications for Owner Financing
When it comes to owner financing, the qualifications a seller might require can vary widely. It’s not a one-size-fits-all scenario, so be prepared for different expectations from different sellers.
Here’s what you might encounter:
- Credit Check – Some sellers will want to see your credit report, just like a traditional lender. They’re looking for a history of responsible financial behavior.
- Income Verification – Sellers may ask for proof of income to ensure you can make the payments. This could include pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements.
- Down Payment – The amount can vary significantly. Some sellers might ask for 20% or more, while others might be open to a lower amount or even no down payment at all.
- Personal Interview – Don’t be surprised if the seller wants to meet you in person. They’re entrusting you with their property, so they may want to get a sense of who you are.
- Property Use Plans – The seller might want to know your intentions for the property, especially if it’s a property they’ve lived in or have an emotional attachment to.
Remember, these are negotiable points. If a seller’s requirements seem too stringent, don’t be afraid to discuss alternatives or look for other opportunities. The key is finding a mutually beneficial arrangement that works for both you and the seller.
Owner Financing: Return on Investment

When you invest in rental properties using owner financing, you can potentially amplify your returns. Let’s break down the four primary returns you’ll earn and how owner financing can impact them:
- Appreciation – This is the increase in your property’s value over time. With owner financing, you still benefit from appreciation, potentially seeing greater returns due to lower initial investment.
- Cash Flow – The money left after paying all expenses. Owner financing can improve cash flow due to potentially lower interest rates and flexible payment terms.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments, you build equity. With owner financing, you might pay down debt faster if terms are more favorable than traditional mortgages.
- Depreciation – A tax benefit that allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value each year. You get this benefit with owner financing.
Additionally, you earn a secondary return on the reserves you set aside for the property. This can be interest earned on savings or investments made with these funds.
Owner financing can significantly impact your returns:
- Lower Down Payments – This can amplify your Return on Investment (ROI) since the down payment is the denominator in the ROI calculation.
- Flexible Interest Rates – Often lower than market rates, improving both cash flow and debt paydown speed.
- Unique Loan Structures – Some owner financing deals may have interest-only loans or balloons, which can improve short-term cash flow but may reduce long-term equity building.
Wrap Financing

Wrap Financing: What is it?
Wrap financing is a creative real estate strategy where the seller acts as the bank, but with a twist – there’s already an existing mortgage on the property.
When you use wrap financing, you’re essentially getting a loan from the seller that “wraps around” their existing mortgage. The seller continues to make payments on their original loan, while you make payments to the seller based on the new, larger loan amount.
Here’s what makes wrap financing unique:
- Existing mortgage stays in place – Unlike owner financing, where the property is free and clear, wrap financing involves a property with an existing loan.
- Two loans, one payment – You make one payment to the seller, who then uses part of that to pay their underlying mortgage and keeps the rest.
- Flexible terms – You and the seller can negotiate interest rates, loan duration, and payment schedules. However, these often need to align with the underlying mortgage terms.
- Potential for lower down payments – Wrap financing can sometimes offer lower down payment options compared to traditional loans.
It’s important to note that wrap financing comes with risks. If the seller doesn’t make payments on the underlying mortgage, you could face foreclosure even if you’ve made all your payments.
Wrap Financing: Return on Investment

When you use wrap financing, you’re tapping into four primary returns on your rental property investment, plus a secondary return. Let’s break these down:
- Appreciation – This is the increase in your property’s value over time. With wrap financing, you benefit from appreciation just like with traditional financing.
- Cash Flow – The money left after all expenses are paid. Wrap financing can potentially improve your cash flow if you negotiate favorable terms with the seller.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments, you’re building equity. There will be two loans (the loan between you and the seller and the loan between the seller and their lender), but you’re only gaining equity from the loan between you and the seller.
- Depreciation – This tax benefit allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value each year, potentially reducing your tax liability.
Additionally, you earn a secondary return on the reserves you set aside for the property. This could be interest earned on savings or investments made with these funds.
The speed and size of these returns in wrap financing can vary. Appreciation and depreciation typically remain consistent with traditional financing. However, cash flow and debt paydown can differ significantly based on the terms you negotiate with the seller.
Remember, while wrap financing shares similarities with owner financing, a key difference is the existing underlying mortgage. The terms of this underlying loan often influence (but don’t always dictate) the terms of your wrap loan. This can impact your returns, especially in terms of cash flow and debt paydown speed.
Key Characteristics of Wrap Financing Sellers
When you’re on the hunt for wrap financing opportunities, you’re looking for a specific type of seller. Let’s dive into what makes these sellers unique and how you can spot them.
First off, wrap financing sellers don’t own their homes free and clear. In fact, a little less than two-thirds of all homes have mortgages. This means there’s a good chance you’ll find potential wrap financing deals out there.
Now, what motivates these sellers? Here are some key characteristics to look out for:
- Long-time listings – Properties that have been on the market for an extended period. These sellers might be more open to creative financing options.
- Vacant properties – An empty house is costing the owner money. They might be eager to find a solution, even if it’s not a traditional sale.
- Out-of-area owners – Managing a property from afar can be challenging. These owners might prefer the steady income of wrap financing over the hassles of long-distance property management.
- Neglected properties – If a home isn’t being maintained, it could signal a motivated seller who’s struggling to keep up with the property.
- Pre-foreclosure situations – Wrap financing could be a potential solution for those facing foreclosure, offering a way out of their financial bind.
- Equity-rich owners – Some sellers might desire a return on their captive equity. Wrap financing allows them to unlock this value while still maintaining some control over the property.
It’s important to note that while these opportunities exist, you should always proceed with caution. My attorney, for instance, doesn’t recommend wrapping FHA or VA loans. Always consult with your own legal counsel before pursuing any wrap financing deal.
Remember, wrap financing is just one tool in your creative financing toolbox. By understanding the characteristics of potential wrap financing sellers, you’ll be better equipped to spot these opportunities and structure deals that work for both you and the seller.
Concerns With Wrap Financing
While wrap financing can be an attractive option for real estate investors, it’s important to be aware of potential concerns. Let’s dive into some key issues you should consider before jumping into a wrap financing deal.
Underlying Loan Payments – One of the biggest concerns with wrap financing is ensuring that the seller’s underlying loan is being paid on time. Here are some strategies to address this:
- Split Payments – Consider making payments in two parts: one directly to the original lender for the underlying loan, and another to the seller for their portion. This ensures the original loan is always current.
- Use an Escrow Service – You can make payments to a third-party escrow service that will handle distributing the funds to both the original lender and the seller. This adds a layer of security and transparency to the process at a slight additional cost.
- Seller’s Credit Risk – Remember, if the seller has excellent credit, it’s still at risk if payments aren’t made properly. This can be a motivating factor for the seller to ensure everything runs smoothly.
Loan Paydown Discrepancies – In rare cases, you might encounter a situation where your wrap loan pays down faster than the original underlying loan. This can happen if the seller’s loan is an interest-only loan or has negative amortization. It can also happen if the interest rates are so different that the amortization schedules lead to you paying down your loan faster than they’re paying down their loan.
To mitigate these risks, consider the following steps:
- Due Diligence – Thoroughly review the terms of both the underlying loan and the wrap loan. Ensure you understand how each loan amortizes and any potential discrepancies.
- Legal Advice – Consult with a real estate attorney who specializes in creative financing. They can help structure the deal to protect your interests and address potential issues.
- Open Communication – Maintain clear, open communication with the seller throughout the process. Discuss any concerns upfront and establish a plan for handling potential issues.
Qualifications for Wrap Financing
When it comes to wrap financing, you’ll find that seller requirements can vary widely. It’s not a one-size-fits-all scenario, so be prepared for different expectations from different sellers. Let’s break down some common qualifications you might encounter:
- Credit and Income Checks – Some sellers will want to ensure you’re financially capable of handling the payments. They might request a full credit report, proof of income, employment verification, and bank statements. However, don’t be discouraged if your credit isn’t perfect. Other sellers may be more flexible, focusing more on your real estate experience or the potential of the deal itself.
- Down Payment – This is often a point of negotiation. Some sellers might ask for 20% or more down, while others might be open to a lower amount. In many cases, you might even find a seller willing to do a no-money-down deal.
- Real Estate Experience – Sellers may be interested in your track record, including previous successful investments, knowledge of the local market, and property management experience. Don’t worry if you’re new to real estate investing. Be honest about your experience level and emphasize your dedication to making the deal work.
- Business Plan – Some sellers might benefit from knowing your plans for the property and exit strategy. This can build rapport and confidence in your ability to keep your agreements.
Remember, these qualifications are all negotiable. If a seller’s requirements seem too stringent, don’t be afraid to discuss alternatives or look for other opportunities. The key is finding a mutually beneficial arrangement that works for both you and the seller.
Loan Assumption

Loan Assumption: What is it?
Loan assumption is a unique creative financing option that allows you to take over the seller’s existing mortgage with the lender’s explicit permission. It’s a powerful tool in your real estate investing arsenal, especially in markets with rising interest rates.
Here’s how loan assumption differs from other creative financing options:
- Lender Involvement – Unlike Subject-To transactions, loan assumptions require the lender’s approval.
- Credit Impact – When you assume a loan, it appears on your credit report.
- Property Ownership – You become the legal owner of the property, with the deed transferred to your name. This is similar to other creative financing options but differs from the Rent-To-Own and Agreement For Deed families of creative financing strategies.
- Loan Terms – Often, you’ll inherit the original loan terms, which can be advantageous if the interest rate is lower than current market rates. However, be prepared for potential fees and qualification requirements.
- Seller’s Position – In most cases, the seller is completely removed from the loan obligation. This clean break can be attractive to sellers looking to move on without lingering financial ties.
Loan assumptions can be particularly attractive in certain scenarios. For example, imagine you find a property with an assumable FHA loan at 3.5% interest, while current rates are at 6%. By assuming this loan, you could save significantly on interest over the life of the loan.
However, keep in mind that loan assumptions often come with challenges:
- Equity Considerations – If the property has appreciated, you may need to finance the difference between the assumed loan balance and the purchase price. This might involve negotiating seller financing or seeking additional funding.
- Qualification Process – Most assumable loans require you to qualify, similar to applying for a new mortgage. Be prepared to demonstrate your creditworthiness and financial stability.
- Limited Availability – Not all loans are assumable. FHA and VA loans are commonly assumable, but conventional loans typically are not.
Loan Assumption: Return on Investment

When you assume a loan, you’re stepping into the shoes of the original borrower. This means you’ll benefit from the four primary returns of rental property investing, plus a bonus return. Let’s break it down:
- Appreciation – Your property’s value may increase over time, potentially at a faster rate in high-demand areas. With loan assumption, you benefit from any appreciation that occurs after you take over the loan.
- Cash Flow – This is the money left after all expenses are paid. Loan assumption can positively impact your cash flow if you’re taking over a loan with favorable terms, such as a low interest rate.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments on the assumed loan, you’re building equity in the property. The speed of debt paydown depends on the loan’s terms and how far into the loan term you are when you assume it.
- Depreciation – This tax benefit allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value each year, potentially reducing your tax liability. You’ll still enjoy this benefit with an assumed loan.
Plus, don’t forget about the secondary return:
- Return on Reserves – The money you set aside for maintenance and unexpected expenses can earn interest, adding to your overall returns.
Loan assumption is similar to owner financing and wraps in that you get appreciation and tax benefits. However, you’re formally taking over an existing loan, often with terms similar to traditional financing.
Here’s where it gets interesting: if you finance all or part of the down payment with the seller for their equity (with the lender’s permission, of course), your return on investment (ROI) could improve significantly. This is because you’re leveraging the seller’s equity to increase your potential returns.
For example, let’s say you’re assuming a $200,000 loan on a $250,000 property. Instead of coming up with the $50,000 difference in cash, you might negotiate with the seller to finance that portion. This could potentially increase your cash-on-cash return and overall ROI.
Remember, always disclose any additional financing arrangements to the lender when assuming a loan. Transparency is key in these transactions.
Key Characteristics of Loan Assumption Sellers
When you’re on the hunt for loan assumption opportunities, understanding the key characteristics of potential sellers can give you a significant edge.
Let’s dive into how to identify possible loan assumption sellers:
- Have an existing loan – This is the foundation of loan assumption. The seller must have a current mortgage on the property.
- Assumable loan – Not all loans are created equal. FHA loans are often assumable, making them a strong candidates for this strategy. VA loans can also be assumable, but they come with additional requirements.
- Owner-occupancy requirement – Here’s a potential hurdle: many assumable loans require you to live in the property. This can be a challenge if you’re looking to invest, but it opens doors for strategies like Nomad™ or house hacking.
- Motivated sellers – Look for properties that have been on the market for a while. These sellers might be more open to creative solutions like loan assumption.
- Vacant properties – A vacant home is costing the owner money. They might be eager to pass on their assumable loan to avoid further expenses.
- Out-of-area owners – Managing a property from afar can be challenging. These owners might prefer the clean break that loan assumption offers.
- Neglected properties – If a home isn’t being maintained, it could signal a motivated seller who’s struggling to keep up with the property.
- Equity-rich owners – Some sellers might have significant equity due to market appreciation or loan paydown. They may be interested in unlocking this value through loan assumption, but may be more challenging for you coming up with paying out their equity. If the underlying loan being assumed allows for financing of the seller’s equity as a second loan, you may be able to negotiate paying out the seller’s equity to them over time. Not all lenders will allow a loan assumption with these second mortgages.
- Attractive loan terms – In a rising interest rate environment, sellers with low-rate assumable loans might ask for a premium. Consider whether paying this premium could still result in long-term savings for you.
- Quick sale desire – Some sellers might prioritize a faster sale over maximizing their profit. Offering loan assumption could be an attractive option for them.
Remember, if the loan isn’t officially assumable, you’re in for an uphill battle. You’ll need to convince the lender to allow the assumption, which can be challenging if not impossible. It may help to consult with a real estate attorney if pursuing a loan assumption on a non-assumable loan.
By keeping these characteristics in mind, you’ll be better equipped to spot potential loan assumption opportunities in your real estate investing journey.
Qualifications to Assume
Loan assumption qualifications vary based on the type of loan and lender requirements:
- Non-qualifying assumable loans: These are rare. No qualification standards apply, simplifying the assumption process.
- Qualifying assumable loans: Lenders typically use traditional lending criteria. You’ll need to meet requirements for creditworthiness, income stability, and debt-to-income ratio.
If the loan maintains recourse against the seller post-assumption, the seller may influence qualification standards due to their ongoing liability.
Communicate clearly with both lender and seller to understand all requirements and negotiate suitable terms.
Seller’s Equity
When you’re considering a loan assumption, it’s crucial to understand how the seller’s equity plays into the deal. In many cases, especially in appreciating markets, the seller will have built up equity beyond the loan balance you’re assuming.
Here’s what you need to know about handling the seller’s equity:
- Down Payment or Monthly Payments – You’ll likely need to compensate the seller for their equity. This can be done either as an upfront down payment or through monthly payments over time.
- Second Position Seller Financing – Often, the equity payment becomes a second mortgage, with the seller essentially financing that portion of the purchase. Fully disclose to the first lender to avoid loan fraud.
- Cash Flow Considerations – Watch out for negative cash flow when structuring these payments. Adding a second mortgage payment on top of the assumed loan could adversely impact cash flow. However, don’t automatically dismiss a deal with potential negative cash flow (which is really just a deferred down payment or financing the down payment over time). Sometimes, the long-term benefits of assuming a low-interest loan can outweigh short-term cash flow challenges.
- Lender Approval – Be aware that the original lender may or may not allow a second position loan for the assumption. Always check with the lender before proceeding with this structure.
Types of Loans to Assume
Some loans are better to assume than others. Consider the following:
- Fixed Rate vs Variable Rate Loans – Fixed rate loans are generally more attractive for assumption, offering stability and predictability. Variable rate loans can add some additional risk.
- Fully Amortizing vs Balloon Loans – Fully amortizing loans are typically preferred as they’re paid off entirely by the term’s end. Balloon loans can be tricky, requiring refinancing or a large payoff at the end.
- Long Term vs Short Term Amortizations – Long term amortizations often offer lower monthly payments, improving cash flow. Short term amortizations build equity faster but come with higher payments.
- Low Interest vs High Interest Rates – Low interest rate loans are highly desirable for assumption, potentially improving your returns significantly. High interest rate loans are less attractive unless you plan to quickly refinance or sell.
- Qualifying vs Non-Qualifying Assumable – Non-qualifying assumable loans are rare but valuable, allowing assumption without a full qualification process. Qualifying assumable loans are more common but require meeting the lender’s requirements.
- Seller Recourse – If you default on the loan, the original seller may still be liable. This can make sellers hesitant to allow loan assumptions without strong buyer qualifications.
- Personal Recourse – Most assumable loans will have personal recourse, meaning the lender can pursue your other assets if you default. Non-recourse loans limiting the lender’s claim to just the property are rare but offer more protection for the borrower.
Rent-To-Own Family

Rent-To-Own: What is it?
The rent-to-own family of creative financing offers a unique approach for real estate investors looking to acquire properties.
- Rental agreement with purchase option – You agree to rent the property from the seller while also securing the right to buy it in the future.
- Flexible terms – You and the seller negotiate the details of the agreement, including rent amount, lease duration, maintenance responsibilities, and often the future purchase price. This flexibility allows you to create a deal that works for both parties.
- Upfront fee – Many rent-to-own agreements require an initial option fee. This fee secures your right to purchase the property and may be applied to the purchase price if you decide to buy.
- Existing financing remains – In most cases, the seller’s current mortgage stays in place. This can be advantageous if the existing loan has favorable terms since the seller may not need higher rent to cover their payments.
- No immediate ownership – As a tenant-buyer, you don’t own the property during the rental period. This means less responsibility but also fewer tax benefits compared to owning outright.
- Variations available – The rent-to-own family includes options like master leases and master lease-options.
Compared to other creative financing options, rent-to-own strategies offer a unique middle ground. They provide more control than traditional renting but less immediate commitment than owner financing or subject-to deals.
This approach can be particularly useful for investors who are concerned about how the market may perform in the future. They can lock in some future upside, but significantly limit their potential downside.
Differences
Rent-To-Own or Lease-To-Own is the umbrella term for arrangements where you rent a property with the potential to own it in the future.
This can take two main forms:
- Lease-Option – You sign a lease agreement with the option to purchase the property at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. This gives you the flexibility to walk away if you decide not to buy.
- Lease-Purchase – In this case, you have a lease agreement coupled with a purchase contract. This typically implies a stronger commitment to buy the property at the end of the lease term. Although you may still have clauses in the purchase contract that allow you not to purchase the property.
The choice between these options can significantly impact your rights and obligations:
- Commitment level – Lease-options offer more flexibility, while lease-purchases often come with a slightly stronger expectation to buy.
- Financial considerations – Both may require an upfront fee, but how it’s applied can differ. In a lease-option, it’s often a non-refundable option fee, while in a lease-purchase, it might be considered earnest money towards the purchase.
- Legal implications – Some attorneys may complicate matters by drafting agreements that include both an option and a purchase contract that activates when the option is exercised. This hybrid approach can offer more protection but also adds complexity.
Remember, the specific terms of your rent-to-own agreement are negotiable. Tailor them to fit your unique situation and goals.
I strongly recommend having an attorney draft your agreement. Once you’ve gone through this process with a lawyer, you may feel more confident making modifications to future agreements on your own. However, always proceed with caution when altering legal documents.
Sandwich Lease-Options
Sandwich lease-options are a sophisticated real estate investment strategy that allows investors to control properties with minimal upfront capital. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how this approach works:
- Initial acquisition – The investor secures control of a property through a lease-option agreement with the original owner. This could be structured as a traditional lease-option, lease-purchase, or in some cases other creative financing options like owner financing, wrap financing, agreement for deed, or subject-to.
- Secondary lease-option – The investor then offers the property to a tenant-buyer on another lease-option basis, creating the “sandwich” structure.
Key financial aspects of sandwich lease-options include:
- Price differential – The investor typically offers the property to the tenant-buyer at a higher price than their agreement with the original owner, creating potential for profit upon sale.
- Rent spread – By charging the tenant-buyer a higher rent than what’s owed to the original owner, the investor generates immediate cash flow.
- Option fees – The investor may collect a substantial, non-refundable option fee from the tenant-buyer, which can offset initial costs and provide upfront returns.
- Negotiated terms – The investor can structure favorable terms on both ends of the deal, potentially including extended option periods or specific purchase conditions.
While sandwich lease-options can be lucrative, they come with significant responsibilities and risks:
- Payment obligations – The investor remains responsible for payments to the original owner, regardless of the tenant-buyer’s performance.
- Legal complexities – These transactions involve multiple parties and agreements, requiring careful legal structuring and documentation.
- Market risk – Changes in property values or market conditions can affect the profitability of the strategy.
Rent-To-Own: Return on Investment

When considering rent-to-own strategies, it’s important to understand how they differ from traditional rental property investments in terms of returns. Unlike most other creative financing strategies, except for the agreement for deed family, you don’t actually own the property in a rent-to-own arrangement. This unique position affects the four primary returns you typically earn on rental properties:
- Appreciation – In a rent-to-own scenario, you might benefit from appreciation, depending on how you structure the deal. If you lock in a purchase price now for a future sale, you could potentially capture the appreciation that occurs during the rental period.
- Cash Flow – You may generate some cash flow from the difference between the rent you collect and any payments you make to the seller. However, this can vary greatly depending on the terms of your agreement.
- Debt Paydown – It’s unlikely you’ll benefit from debt paydown in a typical rent-to-own situation, as you’re not the one holding the mortgage. However, you can structure your deals such that you’re paying the seller a fixed dollar amount above the then current mortgage balance when you buy the property for benefit from debt paydown on their loan.
- Depreciation – You probably won’t receive tax benefits from depreciation since you don’t own the property. This is a significant difference from traditional rental property investments.
Additionally, there’s a secondary return to consider; the return on reserves. If you’ve set aside money as reserves for you might earn a small return on these reserves while they’re waiting to be used.
The speed and size of these returns in a rent-to-own scenario can vary significantly based on your specific agreement. Appreciation (and possibly debt paydown if you’ve structured the deal to include that) might be slower to realize but potentially substantial if property values increase. Cash flow could be immediate but possibly smaller than in a traditional rental. The lack of depreciation benefits and debt paydown can impact your overall returns compared to owning a property outright.
Remember, the structure of your rent-to-own deal is crucial. It determines which of these returns you might access and to what extent. Always carefully consider and negotiate the terms to maximize your potential benefits.
Money Requirements
When it comes to rent-to-own deals, the money required can vary significantly.
- Flexible Seller Requirements – Each seller has unique expectations, which can be both an advantage and a challenge for you as an investor.
- Upfront Money to Seller – This could be earnest money, an option fee, or a security deposit. Some sellers might request as much as 20% down, while others may treat it like a standard rental arrangement. Some may not require an upfront fee at all.
- Negotiable Rent – The agreed-upon rent can vary widely. You might find above-market or below-market rates, depending on the seller’s situation.
While we’ve mainly discussed using creative financing strategies to buy properties, sometimes we offer these options to our buyers as well.
A popular approach is offering a rent-to-own arrangement to a tenant-buyer. In this scenario, you’ll typically set (or at least compare) the monthly rent to what their mortgage payment would be if they financed the property with their down payment at current interest rates, based on their financial situation.
If the tenant-buyer says they can’t afford this monthly rent—which is comparable to what they’d pay with traditional financing—they’re essentially telling you they can’t afford the home.
What happens if you don’t buy?
When entering a rent-to-own agreement as an investor, it’s crucial to understand the potential outcomes if you decide not to complete the purchase.
- Option Fee/Earnest Money/Down Payment – These upfront payments you make are typically non-refundable. They compensate the seller for taking the property off the market. If you don’t proceed with the purchase, you’ll likely forfeit this investment.
- Monthly Payments – The rent you’ve paid isn’t refundable, as it was for occupying the property. However, if you’ve negotiated a portion of your monthly payment as a “rent credit” towards the purchase, you may also lose this credit if you don’t buy.
- Repairs and Improvements – Any repairs or improvements you’ve made to the property generally won’t be compensated if you don’t complete the purchase. It’s crucial to carefully consider any improvements during the rent-to-own period.
- Equity Build-Up – Any equity that has accumulated from paying down the loan typically benefits the seller if you don’t buy. Remember, you’re not the owner until you complete the purchase.
- Lease-Option vs. Lease-Purchase – This distinction is crucial. With a lease-option, you have the right, but not the obligation, to buy. If you don’t purchase, you may only lose your option fee. However, with a lease-purchase, you’re typically obligated to buy unless your purchase contract has clauses to the contrary. Breaking this agreement could result in more severe consequences.
Advanced Strategy for Purchase Price
I mentined this in passing earlier, but let’s dive into an advanced strategy for setting the purchase price when you’re buying a property on a rent-to-own basis.
This approach can help you benefit from debt paydown in a unique way.
Typically, when you enter a rent-to-own agreement, you and the seller agree on a fixed purchase price upfront. For example, you might agree to buy the property for $300,000 in three years.
But here’s where it gets interesting.
Instead of a fixed price, consider negotiating a purchase price that’s tied to the seller’s loan balance.
Here’s how it works:
- Flexible Purchase Price – Instead of agreeing to a set price, you offer to pay the seller’s current loan balance plus a fixed profit at the time of closing.
- Seller’s Profit – For instance, instead of offering $300,000 when the seller owes $290,000 you might agree to pay $10,000 above the current loan balance when you buy the property. Right now, it is $10,000, but that changes over time.
- Benefit from Debt Paydown – As the seller makes mortgage payments, their loan balance decreases. This reduction directly benefits you as the future buyer.
Now, you might be wondering, “How much of a difference can this really make?”
Let’s see:
- Monthly Increase – The amount of debt paid down increases each month as the loan ages. This is because more of each payment goes towards the principal over time.
- Interest Rate Impact – The lower the interest rate on the seller’s loan, the more significant the monthly debt paydown.
- Potential Savings – For a $300,000 home with a 4.5% interest rate, the debt paydown could be around $4,500 per year. If you hold the rent-to-own agreement for three years, that’s an extra $13,500 profit by structuring the deal this way.
Agreement For Deed Family

Agreement For Deed: What is it?
The Agreement for Deed family is a unique set of creative financing options that provides financing without up-front, immediate ownership.
Let’s explore the variations within this family:
- Agreement for Deed – This is the general term for an arrangement where you make payments over time to the seller, but don’t receive the deed until all terms are met. Unlike owner financing, you don’t get immediate ownership, but you do gain equitable interest in the property.
- Bond for Deed – This term is more commonly used in certain regions. It functions similarly to an Agreement for Deed, offering you the opportunity to purchase a property through installment payments without immediate transfer of the title.
- Contract for Deed – Popular in some Midwestern states, this variation follows the same principle as an Agreement for Deed. You agree to pay the purchase price in installments, and the seller agrees to transfer the deed once you’ve fulfilled all the terms.
- Installment Land Contract – This name emphasizes the installment nature of the payments. Like other variations in this family, you gain possession and use of the property while making payments, but the legal title remains with the seller until the contract is fulfilled.
These Agreement for Deed variations differ from other creative financing options in several ways.
- Unlike Rent-to-Own strategies, these are considered sales from day one, even though you don’t receive the deed immediately.
- They also differ from Subject To transactions, as the seller typically retains legal ownership until all payments are made.
- Compared to Wrap Financing or Loan Assumptions, Agreement for Deed options often don’t involve taking over or “wrapping” an existing mortgage. Instead, they create a new financial arrangement between you and the seller.
Agreement For Deed: Return on Investment

When it comes to the Agreement for Deed family, your returns can vary significantly based on how you structure the deal.
Let’s break down the four primary returns you typically earn on rental properties and how they apply to this creative financing strategy:
- Appreciation – With an Agreement for Deed, you might benefit from property value increases over time.
- Cash Flow – Depending on your agreement, you may generate positive cash flow if your monthly payments to the seller are less than the rent you collect.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments, you’re building equity in the property. However, unlike traditional mortgages, you don’t officially own the property until you’ve completed all payments. This makes the debt paydown less tangible in the short term.
- Depreciation – Here’s where Agreement for Deed differs significantly from other strategies. You probably won’t be able to claim depreciation as a tax benefit since you don’t technically own the property until all terms are met. Although if you can demonstrate you have equitable title, you may be able to. Talk to your accountant for details.
Additionally, don’t forget about the secondary return on your reserves. Any money you set aside for maintenance or unexpected expenses can potentially earn interest, adding a small but noteworthy boost to your overall returns.
Remember, Agreement for Deed is most similar to the Rent-to-Own family in terms of how returns work. Your specific returns will depend heavily on how you negotiate and structure the deal with the seller.
Subject-To

Subject-To: What is it?
Subject-to real estate investing is a creative financing strategy where you take ownership of a property while the seller’s existing mortgage remains in place.
Key points:
- Property Transfer – Seller deeds the property to you, making you the legal owner.
- Existing Loan – Original loan stays in seller’s name, not affecting your credit report.
- Lender Notification – Best practice to inform the lender about ownership change.
- Seller’s Credit – Loan continues to appear on seller’s credit report.
Compared to other creative financing:
- vs. Owner Financing – Uses existing loan instead of creating a new one.
- vs. Wrap Financing – With wrap financing the seller can foreclose and take back ownership of the property if you fail to make payments.
- vs. Loan Assumption – No lender approval sought for subject-to.
- vs. Rent-to-Own – Immediate ownership transfer for subject-to.
Subject-To: Return on Investment

When you use subject-to financing, you’re stepping into a unique position that can significantly impact your returns. Let’s break down the four primary returns you can expect from rental properties and how they apply to subject-to deals:
- Appreciation – This is the increase in your property’s value over time. With subject-to, you benefit from appreciation immediately after taking ownership, potentially amplifying your returns if you’ve invested less upfront.
- Cash Flow – This is the money left after all expenses are paid. Subject-to deals can boost your cash flow if you’re taking over a loan with favorable terms, such as a low interest rate.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments on the existing loan, you’re building equity in the property. The speed of debt paydown depends on the loan’s terms and how far into the loan term you are when you take it over.
- Depreciation – This tax benefit allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value each year, potentially reducing your tax liability. You’ll still enjoy this benefit with a subject-to deal.
Subject-to financing is similar to owner financing, wraps, and loan assumptions in that you get appreciation and tax benefits. However, you’re taking over an existing loan without formally assuming it, which can be both an advantage and a risk.
Don’t forget about the secondary return of return on reserves. The money you set aside for maintenance and unexpected expenses can earn interest, adding to your overall returns.
One of the key advantages of subject-to financing is the potential for lower down payments. This can significantly amplify your return on investment (ROI).
Remember, while subject-to can offer attractive returns, it also comes with risks, including the possibility of the lender calling the loan due which we will discuss later.
Creative Financing to…
Creative financing isn’t just a standalone strategy—it’s a versatile tool that can enhance various real estate investing approaches.
While there are numerous variations, we’ll explore a sampling of how you can leverage creative financing to supercharge your investing across different real estate investing strategies.
- Long-term Buy and Hold – Use owner financing or subject-to deals to acquire properties with little money down. This approach allows you to build a portfolio faster, potentially increasing your long-term wealth accumulation.
- Medium-Term Rentals – Utilize rent-to-own to rent a property on a long-term monthly rate and then sublet it at a much higher rate as a medium-term rental.
- Short-Term Rentals – Similar to medium-term rental example above, maybe you opt to leverage a rent-to-own (lease-option agreement) to test the short-term rental market in a specific area before committing to a purchase. If successful, you can exercise your option to buy using more traditional financing.
- Rent-To-Own Exit – Combine the rent-to-own strategy with subject-to financing. You can offer rent-to-own terms to your tenants while making payments on the seller’s existing mortgage, potentially creating multiple streams of profit.
- BRRRR (Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, Repeat) – Use creative financing like owner financing for the initial purchase and rehab phase. Once you’ve added value and stabilized the property, refinance into a conventional loan to pull out your capital for the next deal.
- Fix and Flip – Employ an agreement for deed to secure a property that needs work. This approach can give you the time to renovate and sell the property without the pressure of traditional short-term loans.
Holding
Let’s look at how creative financing performs during your holding period.
Active/Passive
Creative financing strategies in real estate investing tend to be more active than passive.
Here are some reasons why:
- Upfront Work – You’ll need to invest significant time and effort in finding motivated sellers and negotiating deals.
- Deal Structuring – Each creative financing deal is unique. You’ll be actively involved in structuring terms that work for both you and the seller.
- Ongoing Management – Depending on how you creatively financed the property and the strategy utilized, you may need to be more actively involved. For example, buying on a rent-to-own requires you to make a decision and complete the purchase later. However, getting 30-year owner financing will be similar to more traditional financing options.
Duration
When it comes to creative financing in real estate investing, the holding period often depends on the specific strategy you’re using.
Let’s break it down for each variation:
- Owner Financing – This can be a long-term hold strategy. With favorable terms, you might keep these properties indefinitely.
- Wrap Financing – Since there is an underlying loan and a risk of the loan being called due, many real estate investors will prefer to either exit the properties within a relatively short period of time or refinance out of the wrap financing. Of course, if the seller’s underlying loan is paid off in a short period of time and this converts to owner financing it may change the preferred holding period to indefinitely.
- Loan Assumption – This can be a long-term hold strategy similar to owner financing.
- Rent-To-Own Family – These strategies usually have shorter holding periods, often 1-5 years, dictated by the lease term and option period you’ve negotiated. While slightly less likely to be enforced by the lender, the option part of agreement may also trigger the due on sale or due on transfer clause.
- Agreement for Deed Family – If there is underlying financing, this is similar to wrap financing. If there is not underlying financing, this is similar to owner financing.
- Subject To – Due to potential due-on-sale clause risks, many investors aim for shorter holds, often 2-5 years, using strategies like lease-options to exit.
Remember, these are general guidelines. Your specific holding period will depend on your individual goals, market conditions, and the unique terms of each deal. Always have a clear exit strategy in mind when entering any creative financing arrangement.
Exit
What are some of the common you’ll exit out of creatively financed deals? How will your buyers finance them?
Exit Channels
When it comes to exiting properties acquired through creative financing, your strategy can vary depending on the specific method you used. Let’s break it down for each variation:
- Owner Financing – Owner-financed properties offer flexible exit strategies. You can sell traditionally through the Multiple Listing Service (MLS) or For Sale By Owner (FSBO), possibly allowing the new buyer to assume your owner financing agreement. Another option is offering the property on a rent-to-own basis to a tenant-buyer.
- Wrap Financing – Exiting a wrap-financed property needs careful planning. You can sell on the open market via MLS or, more often, offer the property on a rent-to-own basis to a tenant-buyer.
- Loan Assumption – For properties acquired through loan assumption, exit options mirror traditional financing. You can list on the MLS, sell FSBO, or offer a rent-to-own arrangement. The assumed loan might appeal to potential buyers, especially if interest rates have increased since you assumed it.
- Rent-To-Own Family – If you acquired the property through rent-to-own, you might exercise your option to purchase, then use traditional exit strategies. More commonly, you’ll use a sandwich lease-option, offering the property to your own tenant-buyer on a rent-to-own basis.
- Agreement for Deed Family – This approach offers similar exit options to rent-to-own strategies.
- Subject To – Exit strategies here are comparable to wrap financing options.
Exit Financing
When you’re ready to exit your creatively financed property, you have several options for how your buyers might finance the purchase.
- Never sell – You might decide to hold onto the property indefinitely. This strategy can work well if you’ve secured favorable terms through your creative financing, especially with options like owner financing or loan assumption.
- Rent-To-Own – You could offer your property on a rent-to-own basis to your tenant-buyers. This strategy can be particularly effective if you initially acquired the property through a rent-to-own agreement yourself, essentially creating a “sandwich” lease-option or with a strategy with a due-on-sale or due-on-transfer risk where you want to limit your ownership period.
- Traditional Owner-Occupant Loans – If you’re selling to an owner-occupant, they might use conventional, FHA, or VA loans to purchase the property.
- Traditional Non-Owner-Occupant Loans – When selling to another investor, they might use investment property loans. These typically require larger down payments and have slightly higher interest rates compared to owner-occupant loans.
- Cash – Some buyers, particularly investors, might offer to purchase your property with cash. This can lead to a quicker, smoother transaction, which can be advantageous if you need to exit the investment rapidly.
- Owner Financing – If you’ve built up significant equity in the property, you might consider offering owner financing to your buyer. This can be an attractive option if you’re looking for long-term income and are willing to take on the role of the lender.
- Assumption of Your Creative Financing – In some cases, particularly with assumable loans or owner financing, your buyer might be able to step into your shoes and take over the existing financing arrangement. This can be appealing in a rising interest rate environment.

Investor/Entrepreneur
When it comes to Creative Financing in real estate, you’re often walking the line between being a Real Estate Investor and a Real Estate Entrepreneur. Let’s break this down to help you understand where you might fall on this spectrum.
As a Real Estate Investor, your primary focus is on investing money to generate returns. You’re looking at properties as assets that can appreciate over time and provide cash flow. This approach often involves more traditional financing methods and a more hands-off management style.
On the other hand, a Real Estate Entrepreneur is more actively involved in the process. You’re not just investing money, but also a significant amount of time and effort. With Creative Financing, you’re firmly in this entrepreneurial camp. Here’s why:
- Time Investment – You’ll spend considerable time searching for deals, negotiating with sellers, and structuring creative financing arrangements. This isn’t a passive activity; it requires your active engagement.
- Marketing Efforts – To find Creative Financing opportunities, you often need to market directly to motivated sellers. This marketing aspect is a key entrepreneurial activity.
- Deal Structuring – Each Creative Financing deal is unique. You’ll need to craft win-win solutions that work for both you and the seller.
- Problem-Solving Skills – Creative Financing often involves solving complex problems for sellers. This requires entrepreneurial thinking and the ability to see opportunities where others might not.
Remember, while Creative Financing leans heavily towards entrepreneurship, it doesn’t mean you’re not investing money at all as we’ll discuss next.
Money Required
What funds are necessary for creative financing deals? What are the most common financial requirements, and what are some of the less common, more unusual monetary needs?
Most Common
While creative financing often allows for low or no down payment deals, there are still several common expenses you’ll need to consider.
They are:
- Marketing costs – To find motivated sellers open to creative financing, you’ll likely need to invest in marketing.
- Down payment – While some creative financing deals can be structured with no money down, having funds available for a down payment increases your options. Some sellers may require a down payment to feel more secure about the transaction. The more you can offer, the more deals you’ll be able to structure.
- Closing costs – Even with creative financing, you’ll still encounter closing costs. These may include attorney fees for drafting the correct creative financing paperwork, title searches, and recording fees. Be prepared to cover these expenses or negotiate with the seller to share them.
- Rent ready costs – Properties acquired through creative financing may need some work before they’re ready to rent. Set aside funds for repairs, cleaning, and any necessary upgrades to make the property attractive to potential tenants.
- Cumulative negative cash flow – In some creative financing deals, especially those with little to no money down, you might experience negative cash flow initially. This is essentially a deferred down payment since if you put more down you wouldn’t have it. Calculate the total amount of negative cash flow you’re likely to accumulate before rents rise enough to make it positive, and be prepared to cover this shortfall.
- Reserves – Aim to have at least six months of reserves for each property. This cushion helps you handle unexpected expenses, vacancies, or market fluctuations without putting your investment at risk. Remember, each property should have its own reserves – don’t count on using reserves from one property to cover expenses for another.
Less Common
While the most common money requirements for creative financing deals are typically related to down payments, closing costs, and reserves, there are some less common and more unusual ways you might need to use money in these transactions. Let’s explore a few of these options:
- Using option fees from tenant-buyers – When selling via a rent-to-own, you might collect option fees from your tenant-buyers. These fees can sometimes be used to offset your initial costs like marketing to find the deal and more.
- Putting more down or buying all cash – While creative financing often focuses on low or no money down deals, sometimes putting more money down can lead to better terms. For instance, in an owner financing deal, offering a larger down payment might convince a hesitant seller to agree to more favorable interest rates or a longer repayment period.
- Converting creative financing to traditional financing – You might need funds to refinance a creatively financed property into a conventional loan. This could involve paying for an appraisal, covering closing costs, or even putting additional money down to meet loan-to-value requirements set by traditional lenders.
- Substituting collateral – In some creative financing arrangements, you might have the opportunity to substitute collateral. This is a powerful, advanced set of strategies.
Credit Required
When it comes to creative financing in real estate investing, your credit requirements can vary widely depending on the specific strategy you’re using. Let’s break it down:
- Seller Flexibility – Many sellers offering creative financing options won’t require good credit. They’re often more interested in solving their problem (like selling a property quickly) than in your credit score.
- Owner Financing and Wrap Financing – These strategies typically don’t involve traditional lenders, so credit requirements are usually more flexible. The seller might ask to see your credit report, but they’re often willing to work with less-than-perfect credit.
- Loan Assumption – This is where your credit score becomes crucial. To formally assume a loan, you’ll need to meet the lender’s credit requirements, which are often similar to those for a new mortgage.
- Rent-To-Own and Agreement for Deed – Initial credit requirements are often lenient, but remember: if you plan to obtain traditional financing to complete the purchase, you’ll need to meet standard credit requirements at that time.
- Subject To – While the initial transaction doesn’t typically involve credit checks, be aware that if the lender discovers the transfer, they might invoke the due-on-sale clause, potentially requiring you to refinance with good credit.
Remember, while creative financing can offer more flexibility with credit requirements, it’s always beneficial to maintain and improve your credit score. It gives you more options and potentially better terms in your real estate investing journey.
Skills Required
Creative financing in real estate investing requires a specific skill set. Here are the primary skills you’ll need to develop:
- Marketing to Find Flexible/Motivated Sellers – This skill is crucial for sourcing deals. You’ll need to master various marketing techniques to reach potential sellers who might be open to creative financing options.
- Deal Structuring – Once you’ve identified a motivated seller, you must be able to craft a deal that benefits both parties. This involves understanding various creative financing options and knowing when to apply each strategy.
- Deal Analysis – Not every creative deal is profitable. You need to develop a keen eye for analyzing potential investments, including cash flow projections, repair cost estimates, and return calculations under different scenarios.
- Property Management – Understanding tenant screening, maintenance issues, and local landlord-tenant laws is essential. You can gain these skills or hire a professional property manager that has these skills.
These skills are developed through continuous learning, practical experience, and sometimes, learning from setbacks. Mastering them is crucial for success in creative real estate financing.
Stability
When it comes to real estate investing, stability is a crucial factor to consider. Shane Parrish’s concept of active versus passive stability provides a valuable framework for understanding how different strategies, including creative financing, require varying levels of investor involvement.
Creative financing tends to be very actively stable. This means you’ll need to be hands-on and vigilant throughout the investment process. Here’s why:
- Shorter durations – Many creative financing deals have shorter timeframes, requiring you to stay on top of deadlines and exit strategies.
- Non-permanent financing – Strategies like Subject-To deals often involve taking over existing mortgages, which can be called due at any time. You’ll need to be prepared to refinance or sell quickly if necessary.
- Balloon payments – Some creative financing options include balloon payments, where a large sum is due at the end of the loan term. You’ll need to actively plan for this eventuality.
- Interest-only loans – These require careful cash flow management and a solid exit strategy, as you’re not building equity through principal payments.
While creative financing is on the more active end of the spectrum, it’s important to note that real estate investing, in general, is actively stable.
Scalability
Creative financing can be a powerful tool for scaling your real estate investment portfolio. Let’s explore how it compares to other strategies and its potential for growth.
One of the most significant advantages of creative financing is its ability to conserve your capital. Here’s why:
- Lower down payments – Unlike traditional financing that often requires 20% down, creative financing deals can be structured with much smaller down payments, sometimes even zero down. This allows you to acquire more properties with the same amount of capital.
- Marketing cost recovery – When using strategies like lease options, you can often recoup your marketing costs through tenant-buyer option fees. This helps offset your initial expenses and improves your overall return on investment.
- Favorable interest rates – In many creative financing deals, you may be able to negotiate better interest rates than those offered by traditional lenders. This can lead to improved cash flow, making it easier to scale your portfolio.
- Minimal transaction costs – Creative financing often involves lower transaction costs compared to traditional purchases.
However, it’s important to note that creative financing isn’t without its limitations:
- Time constraints – Finding and negotiating creative financing deals can be time-consuming. As you scale, this could become a bottleneck.
- Deal availability – Depending on your market, finding sellers open to creative financing may be challenging, potentially limiting your ability to scale rapidly.
To overcome these limitations and maximize scalability, consider the following strategies:
- Build a team – As you grow, consider hiring employees or contractors to help with deal sourcing, negotiations, and property management. This can help you overcome time constraints and scale more effectively.
- Diversify your approach – While focusing on creative financing, don’t neglect other strategies. A mix of creative and traditional deals can provide a more robust foundation for scaling.
- Leverage technology – Use software and automation tools to streamline your processes, from deal analysis to tenant screening. This can help you manage a larger portfolio more efficiently.
Risk Exposure
When it comes to creative financing in real estate, you’re navigating a landscape filled with both opportunities and potential pitfalls. While these strategies can be incredibly powerful, it’s crucial to understand the risks involved. Let’s dive into the key risk exposures you should be aware of when considering creative financing deals.
Overall, creative financing carries a medium risk rating. This means that while there are significant potential rewards, you need to approach these deals with caution and thorough due diligence.
Here are the main risks you should consider:
- Marketing Costs – Finding creative financing deals often requires extensive marketing efforts. You might need to invest in direct mail campaigns, online advertising, and other marketing to connect with flexible and/or motivated sellers.
- Amplified Returns – Creative financing often involves smaller down payments, which can lead to amplified returns – both positive and negative. While this leverage can boost your profits in a rising market, it also means you’re more vulnerable to losses if property values decline. It’s essential to carefully consider your risk tolerance before pursuing highly leveraged deals.
- Negative Cash Flow Risk – With smaller down payments, you’re more likely to experience negative cash flow, especially in the early stages of your investment. This is essentially a deferred down payment. If you had put more down, you wouldn’t have negative cash flow. While it can be mitigated through negotiating better interest rates or more flexible terms, you need to be prepared for potential short-term losses.
- Market Volatility – Creative financing deals are often more sensitive to market fluctuations. A decline in property values or rental rates during your ownership period can significantly impact your investment’s profitability.
- Due on Sale Clause – Many creative financing strategies can trigger the “due on sale” clause in existing mortgages. If the lender discovers the property transfer, they might demand immediate repayment of the loan, potentially forcing you to refinance or sell the property quickly.
- The “due on sale” or “due on transfer” risk comes from changing ownership or equitable title in a property that has an underlying loan from a traditional lender that has a “due on sale or “due on transfer” clause in the note. Since we define owner financing as when the seller does not have a loan, we don’t have any concern for “due on sale” risk on owner financing. And, since you’re getting the lender’s permission with loan assumption, we’re not concerned about loan assumption either. However, all the other strategies—wrap financing, rent-to-own family, agreement for deed family and subject-to—all include either a transfer of title or equitable title (like an option) on the property and trigger the “due on sale” or “due on transfer” clause.
- Credit Risk – Certain creative financing methods, like loan assumptions can put your personal credit at risk. If you fail to make payments, it could severely damage your credit score, impacting your ability to secure future financing.
- Legal and Ethical Risks – Creative financing deals can be complex, and if not structured properly, you might inadvertently cross into questionable legal or ethical territory. Always consult with a real estate attorney familiar with creative financing to ensure your deals are structured properly.
- Property Management Challenges – Like any real estate investment, you’ll face typical tenant and property management risks. However, these can be amplified in creative financing deals, particularly in rent-to-own scenarios where tenant-buyers might have different expectations than traditional renters.
Profit Speed

When you invest in rental properties using creative financing, you’re tapping into four primary returns plus a secondary return.
Let’s break these down and see how creative financing, in general and depending on the specific strategy, can impact them:
- Appreciation – This is the increase in your property’s value over time. With creative financing, you still benefit from appreciation, potentially seeing greater returns due to lower initial investment.
- Cash Flow – The money left after paying all expenses. Creative financing can significantly improve cash flow due to potentially lower interest rates and flexible payment terms.
- Debt Paydown – As you make payments, you build equity. With creative financing, you might pay down debt faster if terms are more favorable than traditional mortgages.
- Depreciation – A tax benefit that allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value each year. You get this benefit regardless of financing method, but it can be more impactful with creative financing due to potentially lower initial costs.
Additionally, you earn a secondary return on the reserves you set aside for the property. This can be interest earned on savings or investments made with these funds.
The speed and size of these returns in creative financing can vary significantly:
- Immediate Profits – With creative financing, you often see profits immediately. Rents, option fees, or security deposits are typically paid upfront, providing instant cash flow.
- Amplified Returns – Due to lower initial investments, your percentage returns (like Cash on Cash ROI or Cap Rate) can be significantly higher.
- Flexible Cash Flow – Depending on your strategy (e.g., long-term rentals vs. short-term rentals), your cash flow can vary from steady monthly income to larger, less frequent payouts.
Remember, your profits can vary widely depending on your specific creative financing strategy and exit plan. For example:
- Owner-Financing for Long-Term Rentals – You might see steady, growing cash flow over time as you benefit from potentially lower interest rates and flexible terms.
- Subject-To for Short-Term Rentals – Acquire the property creatively and get higher cash flow by utilizing a short-term rental strategy.
- Sandwich Lease-Options – You could benefit from immediate option fees, monthly cash flow spread, and potential lump sum profits at the end of the option period.
Lastly, don’t forget about Cash Flow from Depreciation™. This can provide additional cash flow with each paycheck by adjusting your tax withholdings, or as a lump sum at the end of the year in tax savings.
Creative financing can be a powerful tool to amplify your returns in real estate investing. By understanding these different returns and how they interact with various creative financing strategies, you can make more informed decisions and potentially accelerate your path to financial freedom through real estate.
Finding Deals
How do you find these creative financing deals?
Most Common Methods
Finding creative financing deals often requires looking beyond traditional listings.
Here are the primary methods for finding creative finance deals:
- Actively Marketed FSBOs – Properties advertised directly by owners, often found on websites or with yard signs.
- Hidden FSBOs – Potential sellers not actively marketing their properties. Uncovered through targeted marketing and networking.
More Unusual Methods
While most creative financing deals come from motivated sellers, two less common methods are:
- Wholesalers – Real estate professionals who find off-market properties at discounted prices. Some may have deals with creative financing.
- Multiple Listing Service (MLS) – Occasionally, you can find creative financing opportunities here, especially loan assumptions and owner financing.
Finding Creative Financing Deals
If finding creative financing deals is all about connecting with the right sellers, then what is your primary goal? Locating those flexible, motivated sellers who are open to unconventional selling methods.
How? In a word: marketing.
Marketing is your secret weapon in the quest for creative financing opportunities. It’s all about getting your message in front of potential sellers.
But how you approach this can vary based on your resources and preferences.
Lazy Marketing Methods
While these methods require financial investment, they are strategically efficient approaches to sourcing deals. By allocating resources to targeted marketing efforts, investors can effectively attract potential sellers without expending excessive personal time and energy.
Lazy marketing methods like:
- Direct Mail Campaigns – Send targeted mailings to potential sellers. This could include postcards, letters, or even handwritten notes for a personal touch.
- Outsourced Door-to-Door Marketing – Hire someone to distribute flyers in targeted neighborhoods.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising – Use online ads to target people searching for phrases like “sell my house fast” or “need to sell home quickly.”
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – Optimize your website to rank for keywords related to selling homes quickly or creatively.
- Billboard Advertising – Place eye-catching billboards in high-traffic areas.
- Radio or TV Ads – While more expensive, these can reach a wider audience.
- Print Ads – Consider placing ads in local print publications.
Poor Marketing Methods
If you’re short on cash but long on time and energy, these “poor” marketing methods might be right up your alley. They require more personal effort but can be just as effective.
Poor marketing methods like:
- DIY Door-to-Door Flyers – Distribute flyers yourself.
- Door Knocking – Take it a step further and knock on doors in targeted neighborhoods. Be prepared with a quick pitch and leave behind information if no one’s home.
- Cold Calling – Call for sale by owner properties.
- Driving for Dollars – Drive around looking for properties that appear vacant or in disrepair. Note the addresses and reach out to the owners.
- Online Listings – Post ads on websites or local community forums.
Remember, the key to success in finding creative financing deals is persistence and consistency. Whether you choose “lazy” or “poor” marketing methods (or a combination of both), stick with it. The more potential sellers you reach, the higher your chances of finding that perfect creative financing opportunity.
Analyzing Deals
The World’s Greatest Real Estate Deal Analysis Spreadsheet™ is an essential tool for evaluating creative financing opportunities. This powerful spreadsheet allows you to input various deal parameters and quickly assess potential returns.
By using this tool, you can compare different creative financing structures side-by-side, helping you make informed investment decisions. Don’t let complex calculations hold you back from pursuing creative deals.
Download your free copy of the spreadsheet now and start analyzing your creative financing opportunities with confidence:
https://RealEstateFinancialPlanner.com/spreadsheet
Market Conditions
There are some markets that are better for creative financing deals than others.
Ideal
The ideal market conditions include:
- Markets with motivated sellers – Look for areas where property owners are facing challenges you can solve. These could be sellers dealing with financial distress, inherited properties, or those needing to relocate quickly.
- Favorable price-to-rent ratios – Seek markets where property prices are relatively low compared to potential rental income. This ensures better cash flow and potentially higher returns on your investment.
- Strong appreciation potential – Target areas showing signs of growth, such as improving infrastructure, incoming businesses, or urban development. These factors often lead to property value increases over time.
Challenging
The more challenging market conditions include:
- Hot Seller’s Markets – In extremely strong seller’s markets, property owners can often sell quickly and easily for top dollar, even if their properties are in poor condition. This scenario makes it challenging to negotiate creative financing terms, as sellers have little incentive to be flexible.
- Poor Price-to-Rent Ratios – Markets with unfavorable price-to-rent ratios can make creative financing deals less attractive. When property prices are high relative to potential rental income, it becomes harder to generate positive cash flow, a key consideration in many creative financing strategies.
- Stagnant or Declining Markets – Areas with no appreciation or, worse, negative appreciation in both property values and rents can pose significant risks. In these markets, the potential for long-term gains is limited, which can make creative financing less appealing to both buyers and sellers.
Accessibility/Availability
When it comes to creative financing deals, you’ll need to put in some effort to find them.
These opportunities aren’t always readily available in the MLS, but with consistent effort and the right approach, you can uncover then.
- Aggressive Marketing – Finding creative financing deals at any scale typically requires you to actively market to potential sellers.
- MLS Opportunities – While less common, you may occasionally stumble upon owner financing or loan assumption deals in the Multiple Listing Service (MLS). Keep an eye out for these listings, as they can be valuable opportunities.
- Investor Advertisements – Other investors might advertise rent-to-own deals or other creative financing options to attract tenant-buyers or buyers. In some less common cases these can be potential opportunities for you to step in as an investor.
- Direct Seller Interactions – More often than not, you’ll need to directly engage with flexible or motivated sellers to structure creative financing deals. Building relationships and understanding sellers’ needs is key to success in this area.
Remember, persistence is crucial.
While these deals might not be as readily available as traditional purchases, the potential benefits make the extra effort worthwhile.
Stay proactive, and you’ll increase your chances of finding these unique investment opportunities.
Using Retirement Account
Self-directed retirement accounts are powerful tools for creative real estate financing. These accounts—including self-directed IRAs and 401(k)s—allow investments in various real estate deals, offering flexibility and potential tax benefits. However, strict IRS regulations limit the work you can do on these deals. Additionally, you can’t use self-directed retirement funds to purchase properties you plan to occupy yourself.
Fees Collected From Your Tenant-Buyer
When selling a property on a rent-to-own basis, you’ll typically collect upfront fees from your tenant-buyer. These fees, often in the form of option fees or earnest money, can be viewed in several ways:
Most commonly, the upfront fees you collect will be applied as a down payment when the tenant-buyer purchases the property from you. In essence, you’re receiving a portion of your profit upfront.
- Rebate on Acquisition Costs – Some investors see these upfront fees as a way to offset acquisition costs, including marketing expenses, down payments, and closing fees.
- Improved Cash Flow – Others view these fees as enhanced cash flow, effectively boosting their monthly returns. For instance, a $6,000 down payment for a year-long lease-purchase could be considered an extra $500 per month in cash flow.
- Enhanced Security Deposit – These fees can also serve as an enhanced security deposit, providing financial protection against potential tenant-related issues.
Your approach to these upfront fees will ultimately depend on your investment goals, financial situation, and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
By mastering techniques like owner financing, wrap financing, loan assumption, the rent-to-own family (including lease-option and lease-purchase), the agreement for deed family (including bond for deed, contract for deed, and installment land contract), and subject-to deals, you’re expanding your toolkit and increasing your chances of success. Remember, every deal is unique, and having a diverse set of financing options at your disposal can be a game-changer.
Start small, educate yourself thoroughly, and always prioritize win-win scenarios. With creative financing in your arsenal, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the ever-changing real estate landscape and achieve your investment goals.
So, take that first step. Explore these creative financing options, and don’t be afraid to think outside the box. Your next great real estate deal might just be waiting for a creative solution only you can provide.